An hour's work cost an average of 41.30 euros in 2023 - sixth highest value in the EU
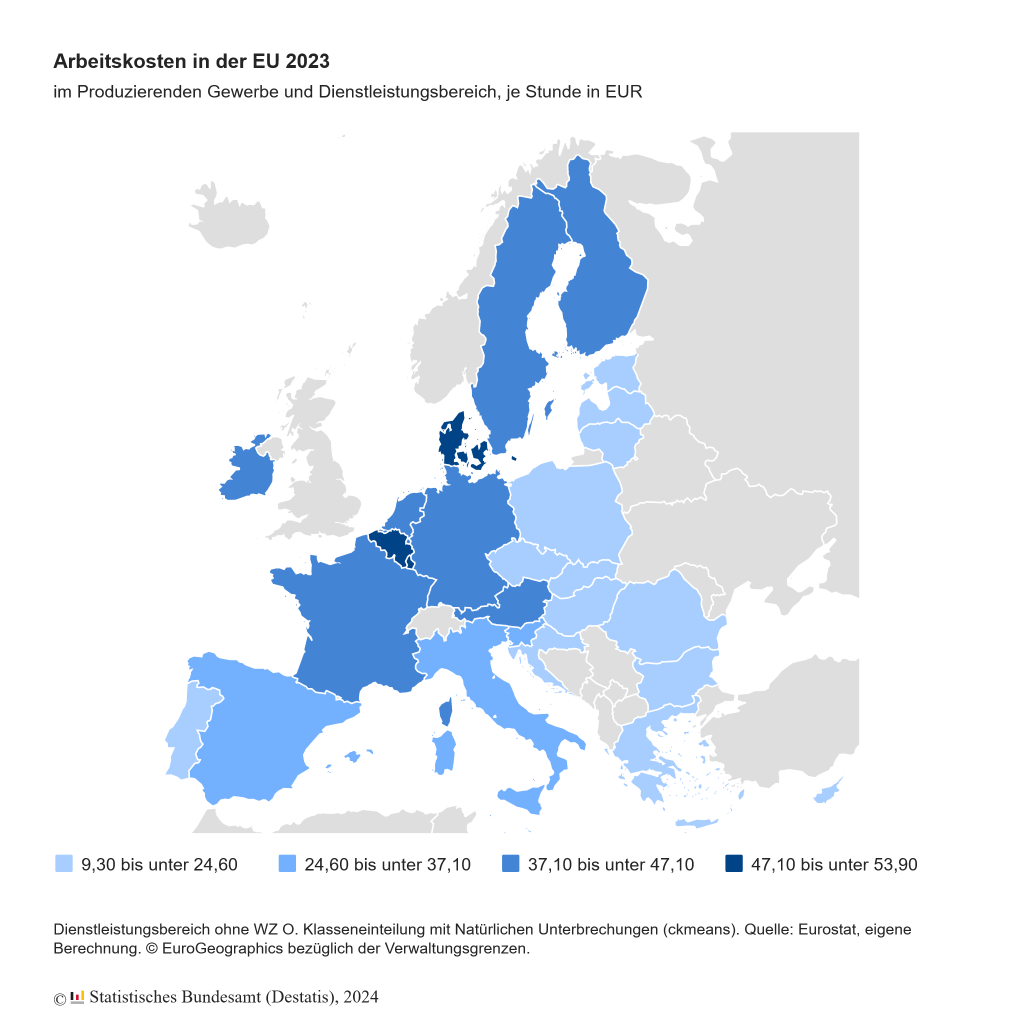
Labor costs in Germany: how high are they compared to the EU average? New figures reveal the cost per hour worked and place Germany in sixth place in the EU
WIESBADEN, April 25, 2024 - The Federal Statistical Office (Destatis) today published data on labor costs in Germany in 2023. Companies paid an average of 41.30 euros per hour worked. This put Germany in sixth place compared to other EU countries.
Labor costs above the EU average
Average labor costs in Germany were significantly higher than the EU average of €31.80 per hour. This means that German employers paid around 30% more for an hour's work than the EU average.
Costs were higher than the EU average in manufacturing and market services in particular. In manufacturing, companies paid an average of 46.00 euros per hour, which is 44% above the EU average of 32.00 euros. In the services sector, costs were also 25% higher than the EU average at €39.80 per hour.
Moderate increase in labor costs in Germany
Compared to other EU countries, the increase in labor costs in Germany remained moderate. While countries such as Hungary, Romania and Poland recorded the highest percentage increases, Germany was slightly below the EU average of 5.3% with an increase of 4.8%.
Variation in labor costs in the EU
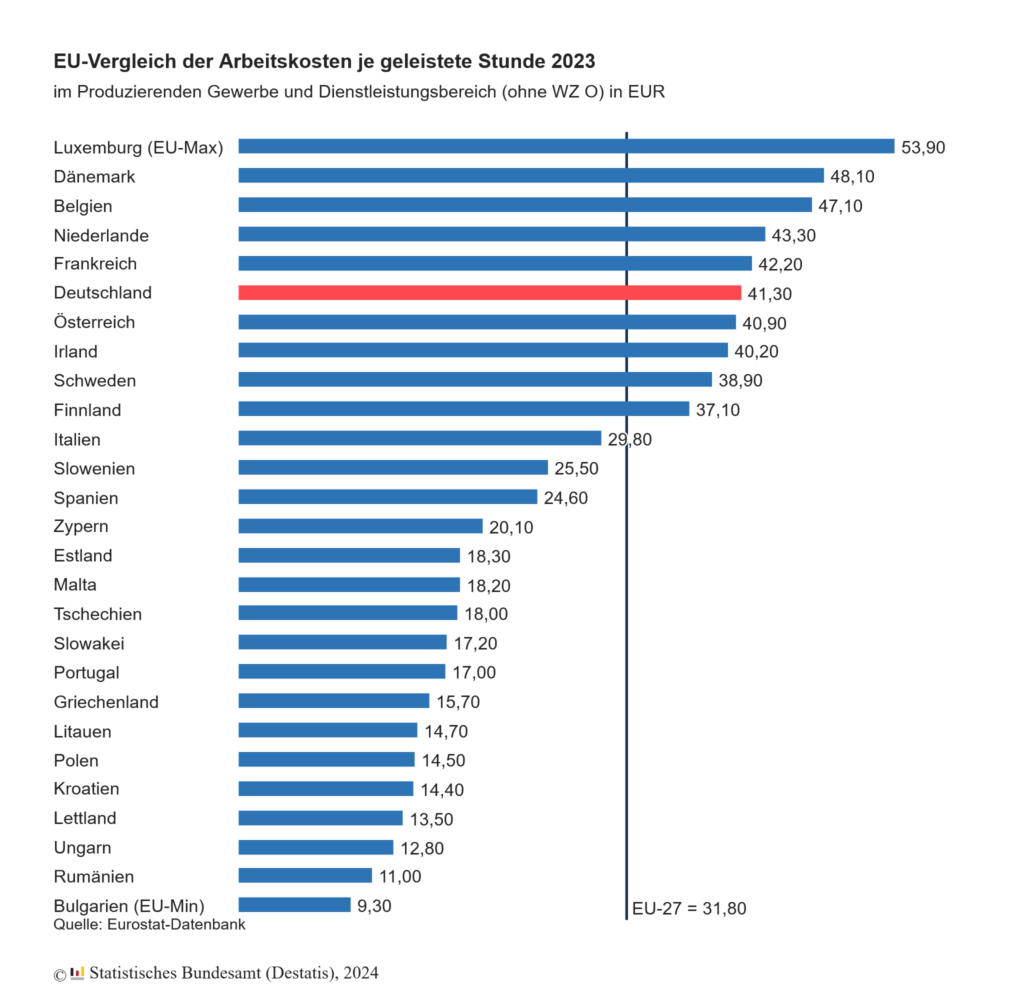
The data shows that labor costs vary greatly across the EU. While countries such as Luxembourg, Denmark and Belgium had the highest costs, Hungary, Romania and Bulgaria were at the lower end of the scale.
Calculation basis - employer gross
The total cost of labor is made up of two main components: gross earnings and non-wage labor costs. Gross earnings include all direct remuneration, including the basic salary, special payments such as bonuses or premiums, additional benefits such as capital-forming benefits and compensation payments for days not worked, such as vacation or public holidays. However, gross earnings do not include continued remuneration in the event of illness. On the other hand, non-wage labor costs include employers' social security contributions, the costs of vocational training and further training, other operating expenses and taxes payable by the employer.
Classification & opinion
When looking at labour costs, it is important not only to consider the pure figures for an hour's work, but also to analyze them in relation to productivity. In the service sector in particular, it is sometimes difficult to achieve a significant increase in productivity, while significant progress can often be made in industry through automation and efficiency improvements. One interesting aspect for future figures is the topic of artificial intelligence. On the one hand, AI offers many industries the opportunity to increase their productivity, while on the other, this tool is available to all markets at the same time. This development could lead to productivity and labor costs developing differently in different sectors and the importance of technology for labor costs increasing further.

Newsletter
Startups, stories and stats from the German startup ecosystem straight to your inbox. Subscribe with 2 clicks. Noice.
LinkedIn ConnectFYI: English edition available
Hello my friend, have you been stranded on the German edition of Startbase? At least your browser tells us, that you do not speak German - so maybe you would like to switch to the English edition instead?
FYI: Deutsche Edition verfügbar
Hallo mein Freund, du befindest dich auf der Englischen Edition der Startbase und laut deinem Browser sprichst du eigentlich auch Deutsch. Magst du die Sprache wechseln?