How employees in start-ups can set up a works council

Flat hierarchies, a foosball table and some beer in the fridge are nice - but if you want to take the concerns of your employees seriously, you need a works council in the long term. Start-ups need to pay attention to this.
With the smartphone bank N26 and the drinks delivery service Flaschenpost, two large start-ups have recently shown how not to do it: in both companies, the employees wanted to set up a works council, but both met with resistance. N26, for example, made negative headlines when founder Valentin Stalf wanted to prevent the ambitions of some employees. According to a report by Finance Forward , the management is said to have written in internal emails that a works council "goes against almost all the values we believe in at N26". A few days later, Stalf apologized, but both parties still argued fiercely about whether such an election was possible in the midst of the coronavirus pandemic. N26 argued that it was too dangerous and wanted to prevent the works council elections in court. The employees, on the other hand, saw the coronavirus pandemic as just a pretext to prevent their plans. In the end, the workforce prevailed and elected a works council in November - officially with the blessing of the founders.
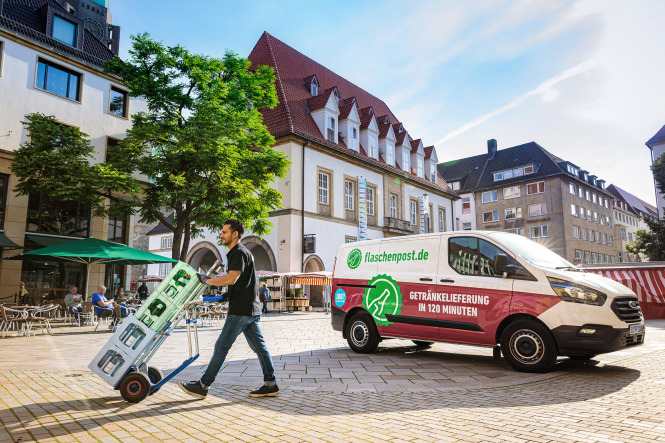
Different company, same game: at the beverage supplier Flaschenpost, the management at the Düsseldorf site initially resisted a works council and took the company to court. However, the regional labor court rejected the complaint and the employees elected their representatives in April.
But why exactly do employees want to set up a works council in start-ups, in which cases is this possible and what can it decide? A look at the most important points.
Why should employees set up a works council?
"People who care about the company also want to set up a works council," says Oliver Hauser, for example, from his experience as a ver.di secretary advising start-ups. This has been proven to improve the atmosphere, reduce staff turnover and integrate the reconciliation of interests into formal structures. "It is important for companies to take a feedback culture seriously and to listen."
However, says Hauser, they should not force a start-up if possible. For example, a works council only becomes a three-member body once there are 21 permanent employees. Before that, it consists of just one person. Alone, they could quickly find themselves caught between the employer and employees.
Who can set up a works council?
Employees in all companies with at least five permanent employees can set up such a representative body - the legal basis for this can be found in the Works Constitution Act. The costs of the works council are always borne by the company.
Who can vote or be elected?
Any employee over the age of 18 may vote, regardless of their position or activity. Senior executives are excluded. "This is difficult for start-ups because they have to define who exactly is a senior employee," says Hauser. As a rough guide, he says: "Senior employees are, for example, people in the company who can hire or fire a person on their own without consultation, or who have great financial influence."
The election committee, which is set up before the works council election and is responsible for the conduct of the elections, decides who is ultimately allowed to vote. It consists of at least three employees entitled to vote and is elected for the first time at a works meeting by the majority of employees present. It can also be appointed by the labor court or a trade union represented in the company.
What are the tasks of a works council?
Working hours in start-ups in particular often call the works council into action: when it comes to weekend work and overtime, the committee must approve them. The works council can also have a say in the furnishing of the premises, working hours and breaks, shift schedules or vacation. It can also have a say when it comes to employee data protection, for example when it comes to tracking or the installation of surveillance cameras and who has access to the data.
What are the limits of a works council?
In Hauser's experience, the issues that concern start-ups are often the hiring and firing of employees. The works council cannot reverse or co-determine the employer's decisions, but it does have the right to a hearing in order to present arguments in favor of a person. Pay is not an issue for the works council. Employment contracts are also not something that works councils deal with. "Of course, the works council can support personal demands to the employer, but it cannot enforce them," explains Hauser.
What do the trade unions have to do with the works council?
Formally, trade unions have no points of contact with works councils. "Works councils can be set up without a trade union," says Hauser. However, elections to the works council in particular are subject to many pitfalls that can lead to invalidity. This is where support is useful. "The employees of start-ups usually approach us," he says. Hauser then advises the election committee, for example, but he also sets limits to his help: "We don't support the election of works councils that serve as vendettas for individual employees."

Newsletter
Startups, stories and stats from the German startup ecosystem straight to your inbox. Subscribe with 2 clicks. Noice.
LinkedIn ConnectFYI: English edition available
Hello my friend, have you been stranded on the German edition of Startbase? At least your browser tells us, that you do not speak German - so maybe you would like to switch to the English edition instead?
FYI: Deutsche Edition verfügbar
Hallo mein Freund, du befindest dich auf der Englischen Edition der Startbase und laut deinem Browser sprichst du eigentlich auch Deutsch. Magst du die Sprache wechseln?